Suppose There Is a Negative Supply Shock
To analyse the supply shock we classify industries as essential or non-essential and construct a Remote Labour Index which measures the ability of different occupations to work from home. Suppose there is a negative supply shock such as due to a flood or earthquake.
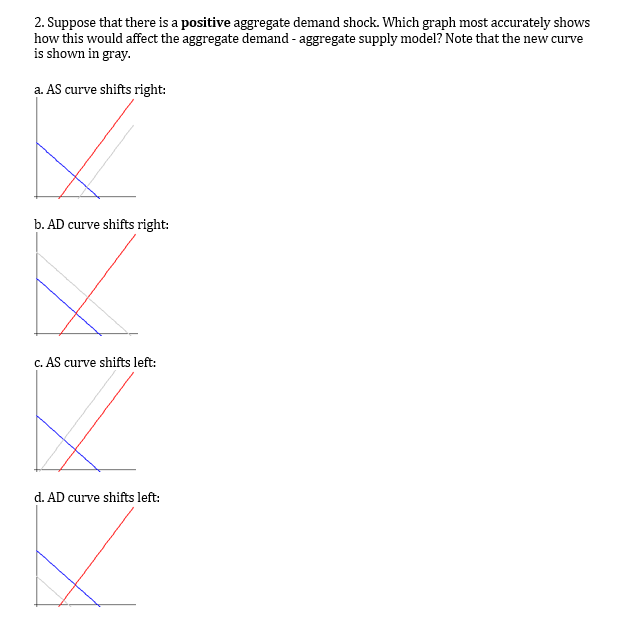
Solved The Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Problem Set1 Chegg Com
Ceteris paribus in the long run a negative supply shock causes.
. Shocks affecting investment spending including changes in bankruptcies business confidence and profit levels. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level a greater quantity of real GDP is produced. Changes in government finances brought about by wars and changes in unemployment.
As a result firms will be willing to supply output only at a higher price. AD curve shifts left. The SRAS to shift to the right.
The AS curve will shift upwards to the left. But if the commitment is not credible then. Any increase in input cost expenses can cause the aggregate supply curve to shift to the left which tends to raise prices and reduce output.
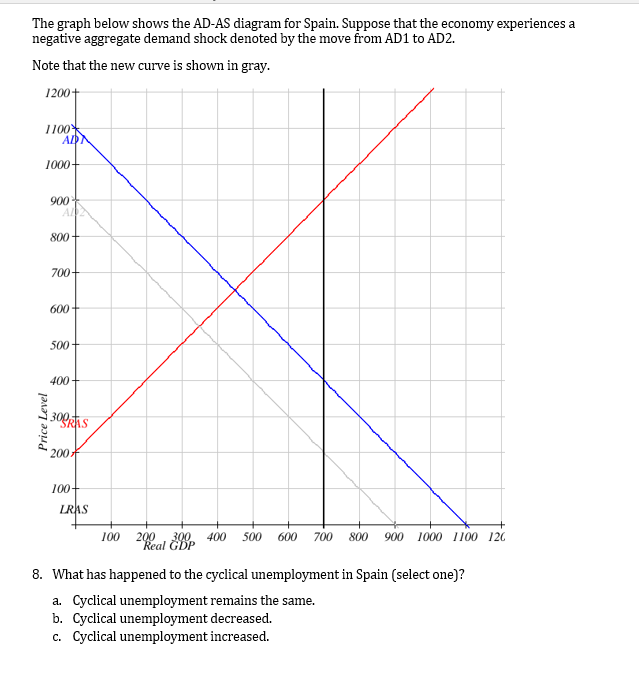
Let SRAS denote the short run aggregate supply curve and let ADdenote the aggregate demand curve. The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift upward economic contraction will be worse. A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2 -Y 3.
The SRAS to shift to the left b. The SRAS to shift to the right c. A graph and an explanation is needed.
Q11 An increase in the price of oil is an example of a negative supply shock. Supply curve and let AD denote the aggregate demand curve. How would this affect the short-run equilibrium price.
This is called a positive supply shock. This module discusses two of the most. Let SRAS denote the short run aggregate.
This is a negative supply shock. In the short run this will cause. A the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift to the left.
This causes the equilibrium to move along the AD curve. D the price level to rise initially and then return to its lower level. In the short run this will cause.
Supply shocks can be negative resulting in a decreased supply or positive yielding an increased supply. AD curve shifts right. Negative shocks or changes to aggregate supply include.
Suppose that there is a negative aggregate demand shock and the central bank commits to an inflation rate target. Suppose that there is a negative supply shock such as an increase in the price of imported oil. When the AS curve shifts to the left then at every price level a lower quantity of real GDP is produced.
According to the real business cycle theory the supply shock will other things being equal A push real Gross Domestic Product GDP upward in the short run but downward in the long run. Figure 1 illustrates the effects of a rapid increase in the price of oil. Note that the new curve is shown in gray.
However theyre often negative. Which graph most accurately shows how this would affect aggreagte demand - aggregate supply model. Shocks directly affecting exports or imports such as the economic collapse of a trading partner.
A If the commitment is credible the publics expected inflation will remain unchanged. There can be many factors that can lead to a negative demand shock. This scenario will lead to.
Because workers can produce only 70 per cent of the output. AS curve shifts right. 1 Answer to 31 Suppose there is an oil supply shock to the US.
It doesnt matter what kind of shock an economy experiences in the standard aggregate demand and aggregate supply model all long-run adjustments are made through changes in aggregate supply Blank 1 Blank 1 supply Correct Unavailable. Suppose that there is a negative supply shock such as an increase in the price of imported oil. This negative real shock would cause the LRAS to shift to the left which causes not only a decrease in GDP but an increase in inflation.
Some of them include. Solution for QUESTION 21 Suppose there is a negative supply shock and the AS curve shifts to the lef. B Credible policy produces better outcomes on both inflation and output in the short run.
Suppose that there is a negative aggregate supply shock. 40 Suppose there is an inflationary gap and the Bank of Canada does not respond in any way to change its monetary policy. Assuming aggregate demand is unchanged a negative or.
Suppose industry i is capable of producing only 70 per cent of its pre-crisis output eg. It is a case of adverse supply shock there is a sudden and significant rise in prices. C equilibrium real GDP to fall.
B unemployment to fall below its short-run level. These two issues recession and high inflation typically require opposite policies from the Fed. Government tax increases Central bank rate increases The cancellation of a government infrastructure project The discovery of a harmful compound in a specific cleaning sanitizer The discovery of a previously unknown side effect of a medicine.
Due to negative supply shock SRAS Stack Exchange Network Stack Exchange network consists of 179 QA communities including Stack Overflow the largest most trusted online community for developers to learn share their knowledge and build their careers. The Bank of Canada validated this negative supply shock with an increase in the money supply whereas in the United States such monetary validation did not take place. Use the AD-AS model graph to explain the effect of a negative supply shock on the price levels and output levels in the economyNote.
Economy due to an embargo by major oil producing nations. 46 Suppose that there is a negative aggregate supply shock and the central bank announces that it intends to hit its established inflation rate target. Negative not credible shift upward contraction is worse.
An increase in the oil price implies an increase in the cost of production. Effects of a Negative Supply Shock. The labour demand curve to shift to the right.
Negative supply shocks have many potential causes. When there is a negative demand shock real GDP falls below the full Blank 1 Blank 1 full Correct Unavailable-employment level and. AS curve shifts left.
The SRAS to shift to the left. - an increase in consumer confidence - a decrease in consumer confidence - an abrupt increase in oil prices - an increase in taxes - a decrease in taxes - a natural disaster.
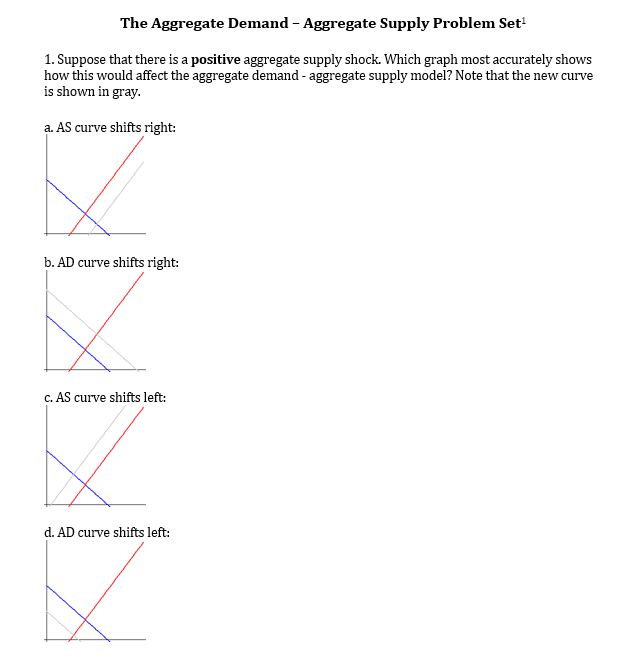
Solved The Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Problem Set1 Chegg Com

Solved The Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Problem Set1 Chegg Com
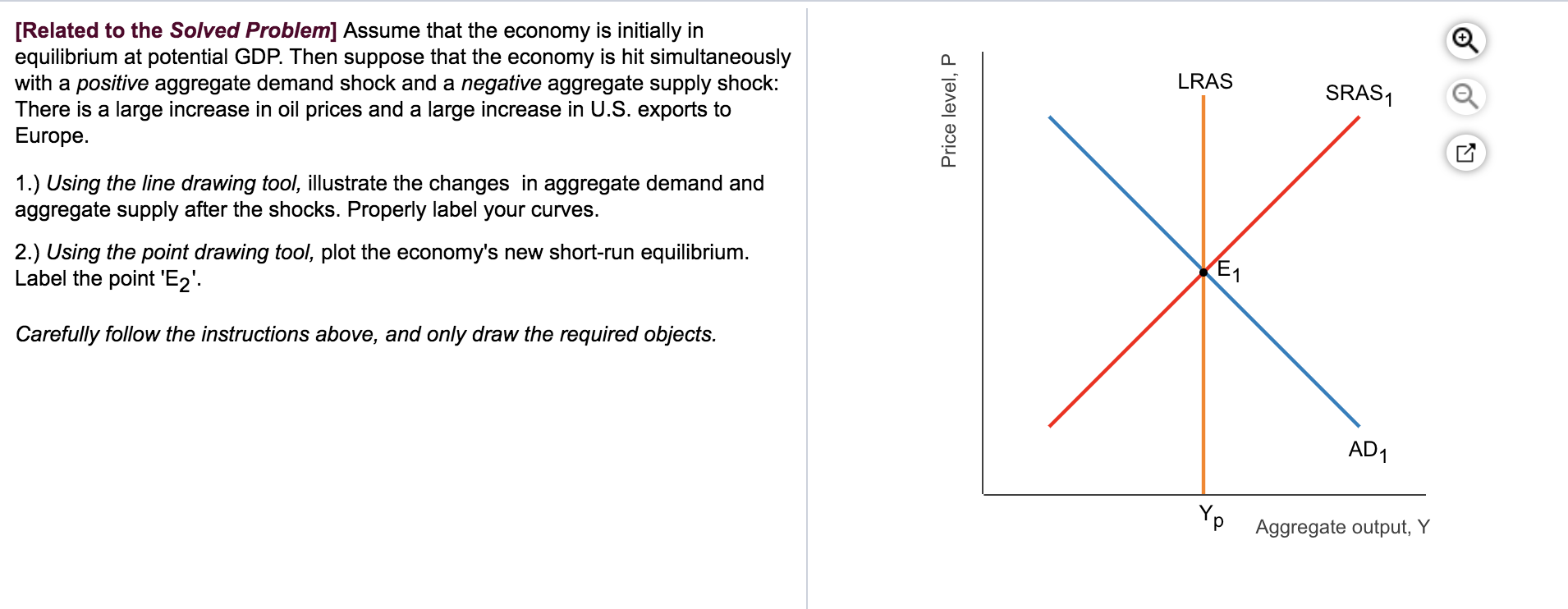
Solved Related To The Solved Problem Assume That The Chegg Com
No comments for "Suppose There Is a Negative Supply Shock"
Post a Comment